Analyzing the Digital Transformation in Malaysia: Impact, Adoption, and Future Trends
Malaysia is going through a major digital transformation which is reshaping various industries across the country. This transformation, fueled by rapid technological advancements and widespread digital adoption, is creating both opportunities and challenges for businesses. This article examines the effects of the digital transformation Malaysia is undergoing on local industries, new technology adoption rates, business challenges, and future trends.The Digital Transformation Landscape in Malaysia
In Malaysia, digital transformation is a multifaceted process that involves integrating digital technology into all aspects of business, fundamentally altering how businesses operate and provide value to customers. In 2024, the household disposable income in Malaysia is forecast to amount to US$235.10 billion, reflecting increasing purchasing power and economic stability, which further drives digital adoption.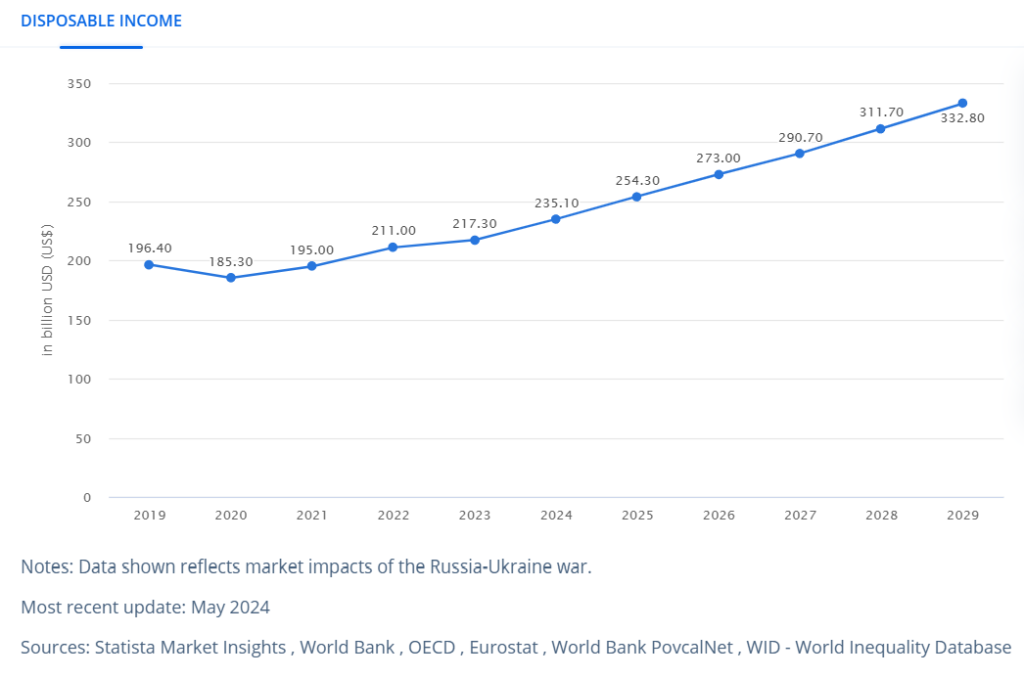
Adoption Rates of New Technologies
At the start of 2024, there were 33.59 million internet users in Malaysia, representing an internet penetration rate of 97.4 percent. This significant penetration rate is indicative of a tech-savvy population ready to embrace new technologies. Mobile commerce is particularly prominent, with consumers increasingly using smartphones for shopping, banking, and entertainment.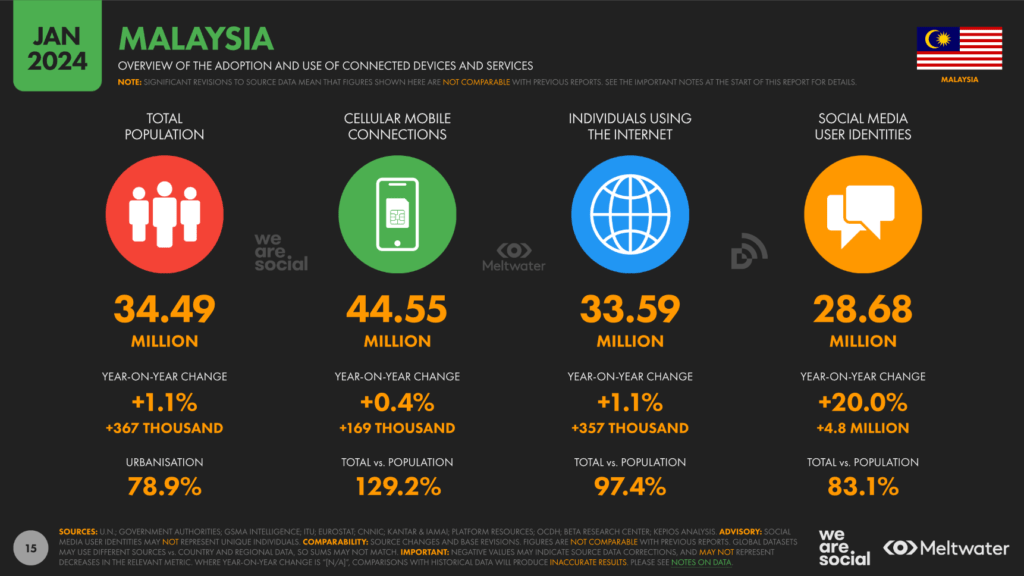 Data from GSMA Intelligence shows that there were 44.55 million cellular mobile connections in Malaysia at the start of 2024, equivalent to 129.2 percent of the total population. Many people use more than one mobile connection for personal and work purposes, which explains the higher number of connections compared to the population. The number of mobile connections in Malaysia increased by 169 thousand (+0.4 percent) between the start of 2023 and the start of 2024.
Between January 2023 and January 2024, the number of internet users in Malaysia increased by 357 thousand, marking a growth rate of 1.1 percent. This surge in internet users highlights the country’s robust digital infrastructure and the increasing reliance on online services. The government’s Malaysia Digital Economy Blueprint further promotes digital transformation by enhancing digital infrastructure and creating a conducive environment for tech-driven growth.
Data from GSMA Intelligence shows that there were 44.55 million cellular mobile connections in Malaysia at the start of 2024, equivalent to 129.2 percent of the total population. Many people use more than one mobile connection for personal and work purposes, which explains the higher number of connections compared to the population. The number of mobile connections in Malaysia increased by 169 thousand (+0.4 percent) between the start of 2023 and the start of 2024.
Between January 2023 and January 2024, the number of internet users in Malaysia increased by 357 thousand, marking a growth rate of 1.1 percent. This surge in internet users highlights the country’s robust digital infrastructure and the increasing reliance on online services. The government’s Malaysia Digital Economy Blueprint further promotes digital transformation by enhancing digital infrastructure and creating a conducive environment for tech-driven growth.
Impact on Various Industries
- Retail: The retail sector has seen a significant shift towards e-commerce, driven by the high internet penetration rate and the convenience of online shopping. Retailers are adopting omnichannel strategies to provide seamless shopping experiences across digital and physical platforms.
- Finance: Digital banking and fintech innovations are transforming the financial industry. Mobile banking, digital wallets, and online payment systems have become mainstream, offering consumers convenient and secure financial services.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine and digital health solutions are becoming increasingly popular, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. These technologies enhance access to healthcare services and improve patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT, AI, and automation, is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector. These technologies improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality.
Challenges Faced by Businesses
Despite the promising advancements, businesses in Malaysia face several challenges in their digital transformation journey.- Digital Skills Gap: There is a shortage of skilled professionals capable of implementing and managing advanced digital technologies. This skills gap hinders the pace of digital transformation Malaysia is experiencing.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As businesses become more digitized, they are increasingly vulnerable to cyber-attacks. To protect sensitive data and maintain customer trust, strong cybersecurity measures must be in place.
- High Implementation Costs: The initial costs associated with adopting new technologies can be prohibitive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Resistance to Change: Organizational culture and resistance to change are significant barriers. Employees and management may be reluctant to adopt new technologies and alter traditional business practices.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of digital transformation in Malaysia.- Increased AI Adoption: Artificial Intelligence (AI) will become more pervasive, driving automation and enhancing decision-making processes across various industries.
- Expansion of 5G: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable internet connectivity, facilitating the adoption of advanced technologies such as IoT and augmented reality.
- Growth of E-Government: The Malaysian government will continue to digitize public services, improving accessibility and efficiency for citizens.
- Sustainability: Digital technologies will play a crucial role in promoting sustainability, enabling businesses to optimize resources and reduce their environmental impact.

