In recent years, Infrastructure Development Malaysia has become a cornerstone of the country’s economic progress. From new highways to sustainable energy projects, the Malaysian government is making significant strides in improving the nation’s infrastructure. These developments are more than just structural upgrades; they are a vital part of Malaysia’s journey toward recovery and growth. The country’s vision for the future includes not only improving connectivity but also embracing sustainability. With careful planning and strong financial backing, Malaysia is positioning itself as a regional leader in infrastructure.
So, how does Infrastructure Development Malaysia drives the country’s construction landscape?
The Role of Infrastructure in Malaysia’s Economic Growth
A key driver of infrastructure development in Malaysia is the construction industry’s projected growth rate of 4.4% per year from 2024 to 2033. This impressive rate is fueled by large investments in key areas like transportation and energy infrastructure. Projects such as the Kuala Lumpur Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system, new highways, and expanding railway networks are set to transform urban mobility. By enhancing connectivity, these initiatives will improve access to essential services and strengthen Malaysia’s position in regional trade.
In 2021 alone, the Malaysian government allocated around $1 billion for infrastructure projects, demonstrating its commitment to economic recovery after the pandemic. These investments are not just about short-term gains; they reflect a broader strategy to enhance the country’s long-term infrastructure landscape.
Significant Contribution to Malaysia’s GDP and Employment
The construction industry plays a significant role in Malaysia’s economy, contributing between 3% to 5% of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This sector is expected to grow as ongoing infrastructure projects come to completion. Not only does this boost the economy, but it also creates many job opportunities.
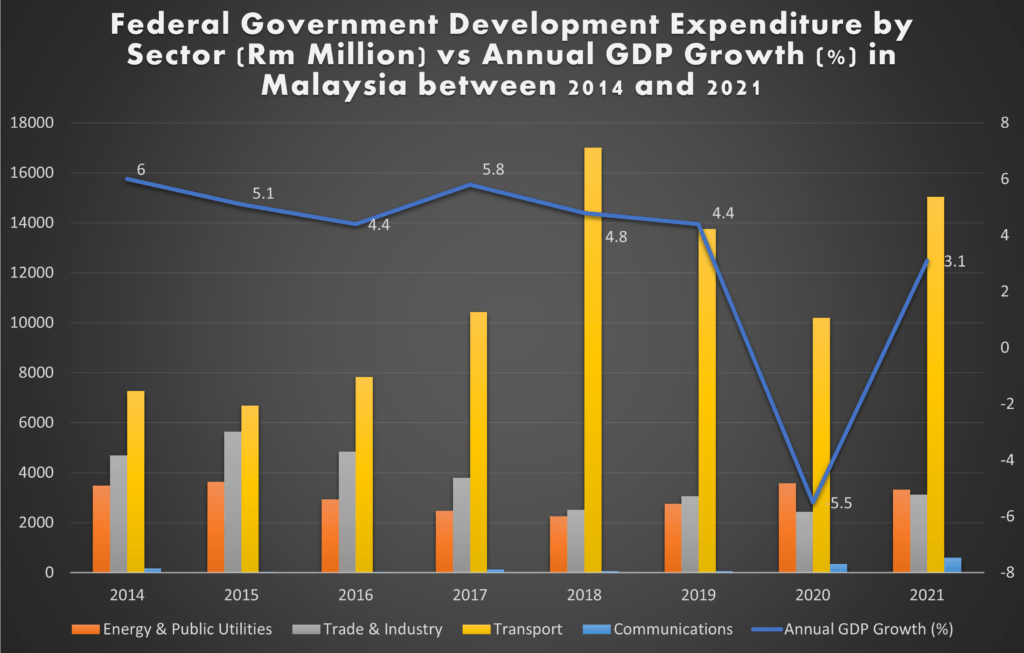
Currently, the construction sector employs about 1.38 million people, making it a crucial source of employment. As infrastructure projects continue to expand, more jobs will be created, further supporting economic recovery. This expansion of employment opportunities underlines how crucial infrastructure development is to both the economic and social wellbeing of the nation.
Focus on Sustainable and Renewable Energy
Malaysia is also looking toward a more sustainable future. The government has allocated approximately $12 million for renewable energy infrastructure projects. This investment will help increase the share of renewable energy in the national grid, further aligning Malaysia with global sustainability goals.
With the rising importance of climate change and environmental sustainability, the focus on renewable energy will play a pivotal role in Malaysia’s infrastructure development. The integration of clean energy into the country’s infrastructure is not only a step toward sustainability but also a means to ensure a stable and secure energy supply for future generations.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Sustainable Funding Model
To fund these ambitious projects, the Malaysian government is increasingly turning to Public-Private Partnerships (PPP). This collaborative model allows for the sharing of costs and expertise between the public and private sectors. By reducing the financial burden on the government, PPPs help ensure that infrastructure projects are completed efficiently and within budget.
This approach has already proven successful, attracting both domestic and international investors. With more private-sector involvement, Malaysia can expect even faster completion of infrastructure projects, which will further stimulate economic growth.
Transport Infrastructure: Expanding Malaysia’s Connectivity
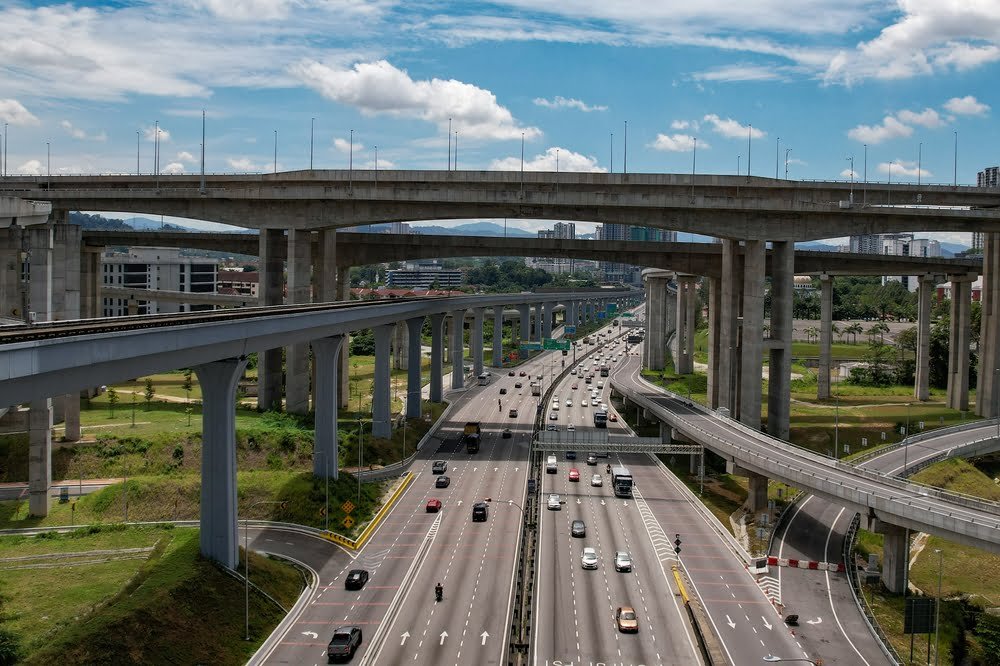

Transport infrastructure remains one of the most critical sectors for Malaysia’s infrastructure development. Between 2010 and 2015, the country’s road network expanded by 68%, dramatically improving connectivity across various regions. This expansion enables better access to services, education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, especially in rural areas.
By improving transportation networks, Malaysia is better positioned to compete in regional and global markets. Enhanced transport infrastructure also strengthens trade routes, making it easier for goods to move across borders, which is essential for Malaysia’s export-driven economy.
In conclusion, Infrastructure Development Malaysia is not just about building roads and bridges; it’s about laying the foundation for the country’s future growth and prosperity. The expected 4.4% annual growth rate in the construction industry, coupled with public-private partnerships, ensures that these projects will not only enhance Malaysia’s infrastructure but also create jobs and support long-term economic recovery. As Malaysia continues to invest in infrastructure, the country is on track to becoming a regional leader in economic development and sustainability.

