Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) have been a vital part of Malaysia’s infrastructure development since the mid-1980s. This model was introduced as a joint venture between the government and private sector to boost the country’s economic growth. The concept of Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia gained momentum under the leadership of Tun Dr. Mahathir Mohammad. He adopted this model from the United Kingdom’s privatization policies.
Over the years, Malaysia has seen substantial growth in its infrastructure through this collaborative approach, leading to the development of over 1,800 kilometers of toll highways by the early 2000s. Let’s take a deeper look into this!
Success Stories of Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia
Public-Private Partnerships have made a significant impact on Malaysia’s infrastructure landscape, particularly in building essential infrastructure such as highways, schools, and economic zones. Malaysia’s reliance on the private sector for toll road construction has been one of the standout achievements of PPPs. More than 25 highways have been privatized under this model, effectively meeting the country’s growing infrastructure demands.
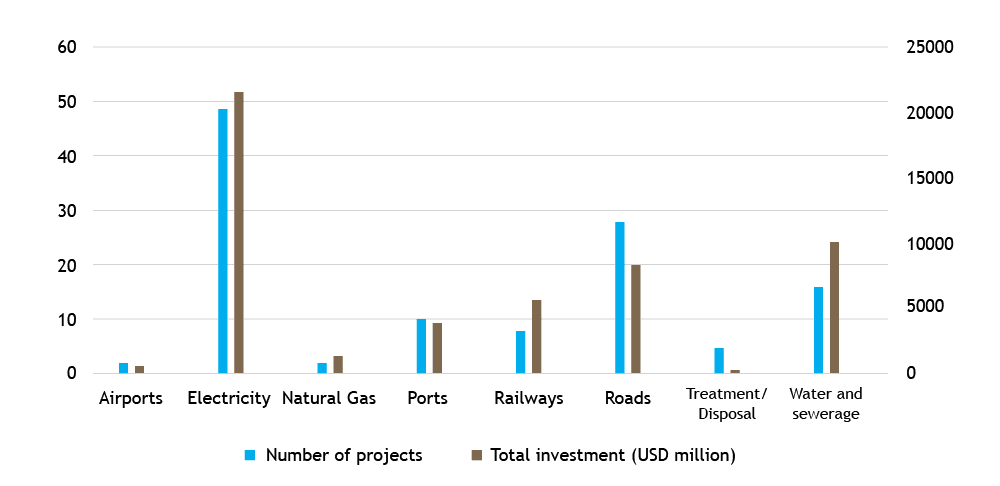
This Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia model has enabled the country to push forward on large-scale infrastructure projects without overburdening the government’s budget. By sharing risks and responsibilities between the public and private sectors, Malaysia has been able to maintain a steady pace of development while promoting economic growth.
Infrastructure Development and Economic Growth
The role of Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia in the economic growth became even more crucial following the Asian financial crisis in the late 1990s. During this period, Malaysia adopted a series of measures aimed at stabilizing the economy and driving long-term growth. PPPs became a key element of these strategies, as outlined in the Ninth Malaysian Plan. This plan included the use of PPPs as a method to finance and manage various infrastructure projects. Amongst many projects, includes building schools, government offices, and special economic zones.
The economic rationale behind PPPs lies in their ability to spread the financial burden between the government and private companies. As a result, large-scale projects are becoming more feasible. These collaborations also promote efficiency and innovation, as private companies are incentivized to meet performance targets and complete projects on time and within budget.
Challenges Faced by PPP Projects
Despite the successes of PPPs, Malaysia has encountered several challenges in implementing these projects. One of the key issues is the lack of clear guidelines for managing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which are essential for measuring the success of any infrastructure project. The absence of a robust framework for monitoring project performance and transparency in the tendering process has often led to delays and inefficiencies.
For example, many Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia projects suffer from service delivery failures due to inadequate maintenance strategies. These failures are often linked to the fragmented nature of PPP contracts, where different entities are responsible for the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure. This lack of cohesion has resulted in poor long-term planning, which affects the sustainability and effectiveness of these projects.
The Future of Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia
Looking ahead, Public-Private Partnerships Malaysia are expected to continue playing a critical role in Malaysia’s infrastructure development. As the country seeks to maintain its economic growth and improve public services, PPPs offer a viable solution for meeting the financial and technical demands of large-scale projects. The government is committed to refining the PPP model to address current challenges, such as enhancing transparency, improving maintenance practices, and developing better performance metrics.

