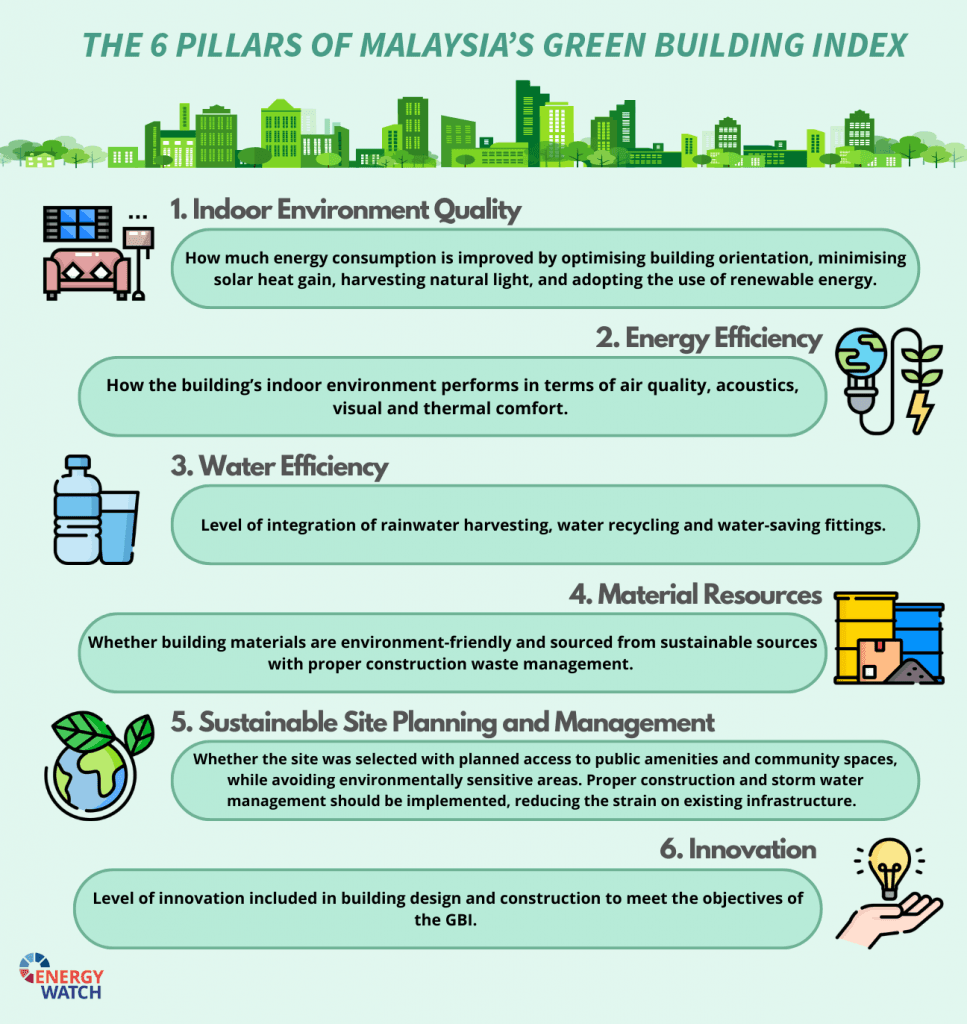
Malaysia is making bold strides in sustainable development through the promotion of Malaysia Green Building Projects. A major driver behind this shift is the Green Building Index (GBI), launched in 2009 by the Malaysian Institute of Architects and the Association of Consulting Engineers Malaysia. GBI is a globally recognized green building certification that assesses and promotes sustainable construction practices in Malaysia. Alongside GBI, the country also recognizes other certifications like GreenRE and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), which further evaluate and endorse eco-friendly designs.
Eco-Friendly Materials Powering Malaysia Green Building Projects
Malaysia Green Building Projects are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly materials to reduce the carbon footprint of new developments. Among the standout materials gaining popularity are bamboo and recycled steel. Bamboo is strong, versatile, and rapidly renewable, making it ideal for structural applications. Meanwhile, recycled steel offers significant environmental benefits over newly produced steel.
Other materials such as rammed earth and aerated concrete are also gaining traction for their energy efficiency. These materials offer excellent insulation properties, contributing to reduced energy consumption in buildings. Furthermore, techniques like green roofs and rainwater harvesting systems are becoming more common. These not only enhance the aesthetic value of urban areas but also contribute to biodiversity and help manage stormwater, significantly reducing urban heat.
Energy-Efficient Designs and Green Architecture
Buildings are responsible for nearly half of global annual CO2 emissions, and Malaysia is working to combat this by integrating energy-efficient designs into its construction projects. With urban populations expected to rise dramatically, sustainable architecture is no longer just an option but a necessity.
Leading examples of Malaysia Green Building Projects include the University of Technology Sarawak, which received a GBI Platinum rating for its eco-friendly design. Then there are the Nucleus Tower and Tropicana Gardens Mall, which also showcase energy-efficient features. These projects are paving the way for other developments across Malaysia, demonstrating how green buildings can reduce environmental impact.
Government Initiatives Fueling Malaysia Green Building Projects
The Malaysian government is playing a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of Malaysia Green Building Projects through a series of policies and financial incentives. Initiatives like the Green Technology Financing Scheme and various green tax incentives have created a favorable environment for developers to invest in sustainable projects.
Moreover, the government is integrating sustainability into the national education system, ensuring that future generations are well-versed in green technology. Specialized courses related to sustainability are now being offered in public and private universities, and green skills are being incorporated into national occupational standards. This commitment will ensure that Malaysia has the expertise it needs to continue expanding its green building initiatives.
Malaysia’s Path to a Sustainable Future
As Malaysia continues to urbanize, the construction industry plays a pivotal role in the country’s social and economic development. The industry contributes 2.1% to Malaysia’s GDP and provides jobs for around 800,000 people, making it a critical part of the economy. By incorporating sustainable practices into this sector, Malaysia is setting itself up for long-term growth that balances economic needs with environmental preservation.
Malaysia Green Building Projects are not just a trend—they represent a significant movement toward a greener, more sustainable future. With a strong framework of government support, innovative use of eco-friendly materials, and collaborations between developers and utilities, Malaysia is positioned to be a leader in sustainable construction in the region. By fostering these initiatives, Malaysia is not only reducing its carbon footprint but also inspiring future generations.

